Research : VKOR-complex
Identification of the Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase (VKORC1)
Christof Geisen, Katja Sittinger, Gabriele Spohn (Frankfurt)Andreas Fregin, Clemens Müller-Reible, Simone Rost (Würzburg)
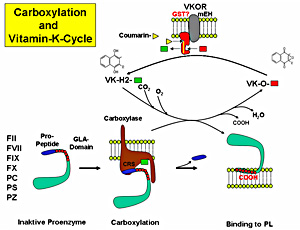
Coumarins represent the only drug for oral anticoagulant therapy in the treatment and prevention of thromboembolic disorders. Although prescribed for over 60 years the molecular mechanism remained unknown. We recently have identified VKORC1 which represents the target of coumarin (Fregin & Rost 2002, Rost & Fregin 2004). VKORC1 is located on the short arm of chromosome 16 close to the centromer. While homozygous missense mutations within VKORC1 are responsible for the deficiency of all vitamin K dependent coagulation factors type 2 (VKCFD2), heterozygous missense mutations cause warfarin resistance (WR) in human and in rats. This project is intended to lead to a better understanding of the structure of the vitamin K cycle and an improved drug design for coumarins.
